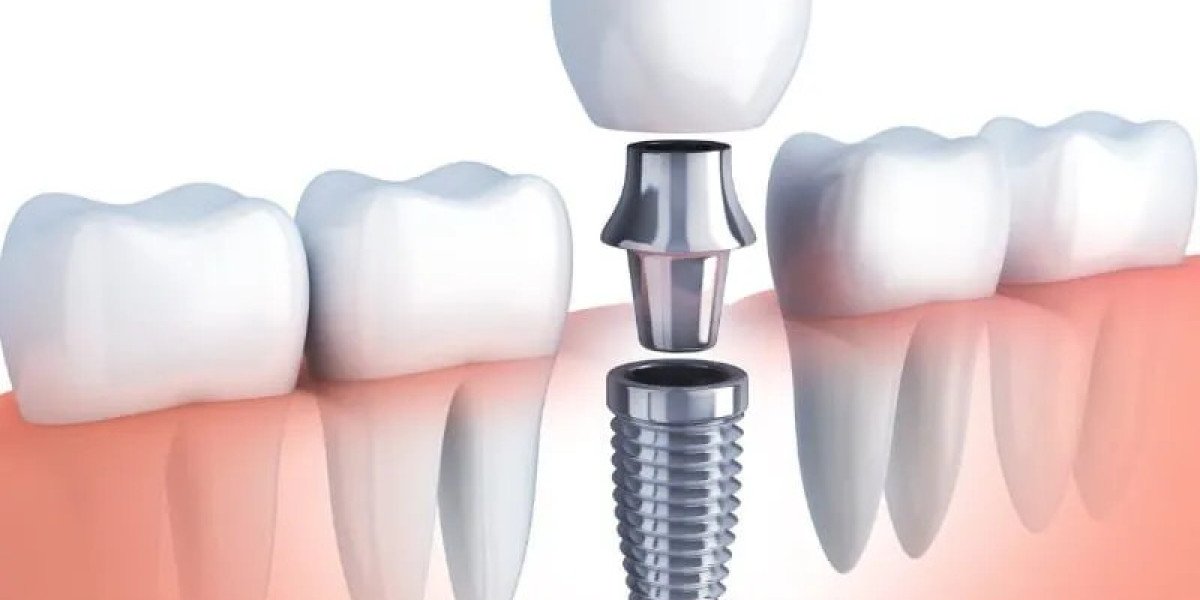
Bone grafting is a common dental procedure used to restore or augment bone tissue in the jaw, often necessary for dental implants, repairing bone defects, or treating periodontal disease. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the purpose of bone grafting, the different types of bone grafts, the procedure itself, benefits, potential risks, and recovery process.
1. Purpose of Bone Grafting:
- Bone Regeneration: Bone grafting helps stimulate new bone growth or repair damaged bone tissue in the jaw, providing a stable foundation for dental implants or other restorative procedures.
- Implant Placement: In cases where there is insufficient bone volume or density in the jaw, bone grafting may be necessary to create a suitable environment for successful dental implant placement.
- Preservation of Jaw Structure: Bone grafting can help prevent bone loss and Dentist in Mckinney preserve the natural contours of the jaw following tooth extraction or periodontal disease.
2. Types of Bone Grafts:
- Autogenous Bone Grafts: These grafts involve taking bone tissue from another part of the patient's body, such as the hip or jaw, and transplanting it to the area requiring augmentation.
- Allografts: Allografts use bone tissue from a human donor, typically obtained from a tissue bank, which is processed and sterilized before transplantation.
- Xenografts: Xenografts utilize bone tissue from animals, usually bovine or porcine sources, Oral Appliances which is processed to remove organic materials and sterilized for use in humans.
- Synthetic Bone Grafts: Synthetic bone graft materials, such as calcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite, mimic the properties of natural bone and are used as an alternative to traditional grafting materials.
3. Bone Grafting Procedure:
- Consultation and Evaluation: The dentist or oral surgeon will evaluate the patient's oral health, medical history, and bone quality through imaging techniques such as X-rays or Dentist near me CT scans.
- Graft Material Selection: Based on the patient's needs and the desired outcome, the appropriate type of bone graft material will be selected.
- Surgical Procedure: The bone grafting procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia. The dentist or oral surgeon will make an incision in the gum tissue to access the bone and prepare the site for graft placement.
- Graft Placement: The bone graft material is carefully placed into the defect or area of bone loss and secured in position. In some cases, a barrier membrane may be used to protect the graft and promote healing.
- Suturing: The incision site is sutured closed, and Sleep Apnea the patient is provided with post-operative instructions for care and recovery.
4. Benefits of Bone Grafting:
- Improved Implant Success: Bone grafting enhances the success rate of dental implants by providing a stable foundation for implant placement and osseointegration.
- Preservation of Facial Structure: Bone grafting helps prevent bone loss and preserve the natural contours of the jaw, preventing the appearance of premature aging and facial collapse.
- Restoration of Function: Bone grafting restores proper jaw function, enabling patients to chew, speak, and Teeth Grinding smile with confidence.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: By restoring lost bone volume and density, bone grafting improves the aesthetics of the smile and facial profile.
5. Risks and Considerations:
- Infection: Like any surgical procedure, bone grafting carries a risk of infection, which can typically be managed with antibiotics and proper post-operative care.
- Graft Failure: In some cases, the graft may fail to integrate with the surrounding bone tissue, Family Orthodontics requiring additional grafting procedures or alternative treatment options.
- Pain and Discomfort: Patients may experience temporary pain, swelling, and discomfort following bone grafting surgery, which can be managed with pain medication and ice packs.
- Cost: The cost of bone grafting varies depending on the type of graft material used, the extent of the procedure, and other factors, so patients should discuss financial considerations with their dentist or oral surgeon.
6. Recovery Process:
- Initial Healing: Patients may experience swelling, bruising, and Clearcorrect discomfort in the days following surgery, which typically subsides within a week.
- Dietary Restrictions: Soft foods and liquids are recommended during the initial healing period to avoid placing excessive pressure on the graft site.
- Oral Hygiene: Patients should maintain good oral hygiene practices, including gentle brushing and rinsing with a saltwater solution, to keep the surgical site clean and promote healing.
- Follow-up Appointments: Patients will schedule follow-up appointments with their dentist or Teeth Braces oral surgeon to monitor healing progress and evaluate the success of the bone graft.
Conclusion: Bone grafting is a valuable tool in modern dentistry for restoring lost bone tissue, enhancing the success of dental implants, and preserving facial structure and function. By understanding the purpose of bone grafting, the different types of graft materials available, the procedure itself, potential risks and benefits, and the recovery process, patients can make informed decisions about their oral health and Sedation Dentistry treatment options. If you are considering bone grafting or have questions about the procedure, consult with a qualified dental professional to discuss the best course of action for your individual needs and goals.
 AdBlock Detectado
AdBlock Detectado