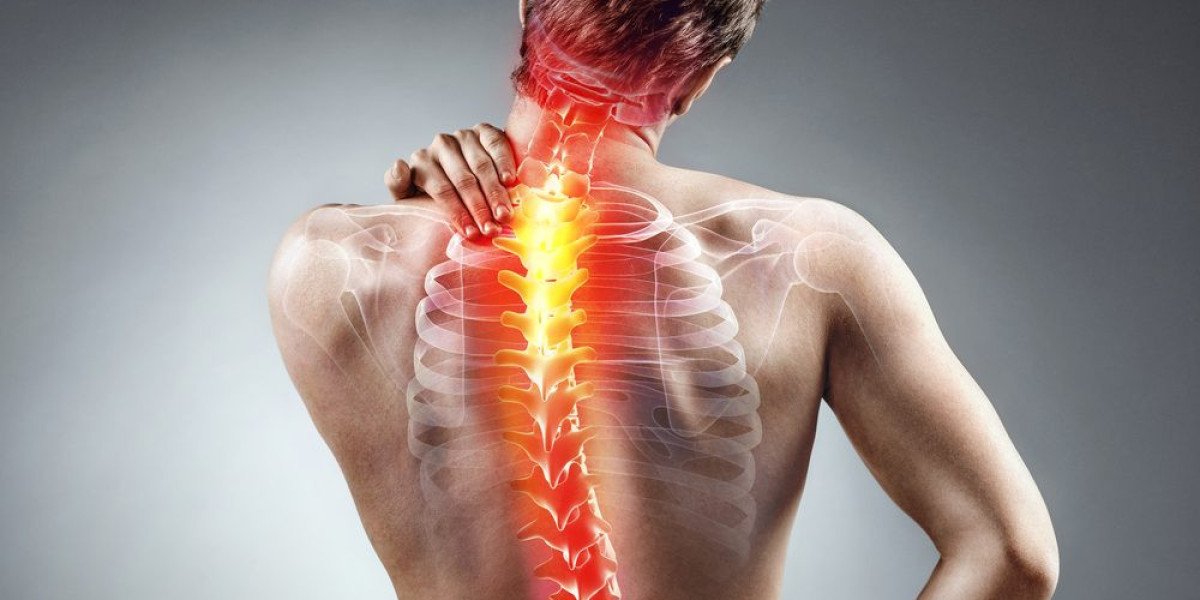
Muscle pain, whether acute or chronic, can significantly impact daily life, hindering mobility and diminishing quality of life. Fortunately, advances in medical science and holistic approaches have paved the way for modern strategies that effectively target muscle pain at its root. In this comprehensive guide, we explore a range of contemporary approaches to treating muscle pain, encompassing both conventional and alternative modalities.
Muscle Pain:
Before delving into treatment options, it's crucial to understand the underlying mechanisms of muscle pain. Muscle pain, or myalgia, can stem from various factors, including overuse, injury, tension, inflammation, or underlying medical conditions such as fibromyalgia or myofascial pain syndrome. Effective treatment requires a personalized approach that addresses the specific cause and nature of the pain.
Modern Treatment Approaches:
Physical Therapy and Exercise:
Targeted exercises and stretching routines prescribed by a physical therapist can help alleviate muscle tension, improve flexibility, and strengthen supporting muscles.
Techniques such as myofascial release, trigger point therapy, and manual therapy can target specific areas of muscle tightness or dysfunction, providing relief and promoting healing.
Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Pain O Soma 500, Prosoma 500, ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with muscle injuries or conditions such as tendonitis or bursitis.
Muscle relaxants may be prescribed for acute muscle spasms or persistent tension, providing relief by inhibiting muscle contractions and promoting relaxation.
Regenerative Therapies:
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and stem cell injections offer regenerative potential by harnessing the body's natural healing mechanisms to repair damaged muscle tissue and reduce inflammation.
Prolotherapy involves injecting a solution (often dextrose) into damaged ligaments or tendons, stimulating the body's healing response and promoting tissue repair.
Electrotherapy:
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) use electrical currents to modulate pain perception, promote muscle relaxation, and enhance circulation to the affected area.
Mind-Body Techniques:
Practices such as yoga, tai chi, and meditation can help alleviate muscle tension, reduce stress, and promote overall well-being, complementing other treatment modalities.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) may be beneficial for individuals with chronic muscle pain, helping them develop coping strategies, manage stressors, and improve their psychological resilience.
Integrative Approaches:
Combining various modalities such as acupuncture, massage therapy, and herbal supplements can offer a holistic approach to managing muscle pain, addressing both physical and emotional aspects of discomfort.
Conclusion:
In the modern era, the treatment landscape for muscle pain has evolved significantly, offering a diverse array of options tailored to individual needs and preferences. From conventional approaches like physical therapy and medication to innovative therapies such as regenerative medicine and electrotherapy, there are numerous avenues for alleviating muscle pain and promoting recovery. By embracing a multidisciplinary approach that integrates evidence-based practices with holistic strategies, individuals can regain control over their musculoskeletal health and embark on a journey toward pain-free living.