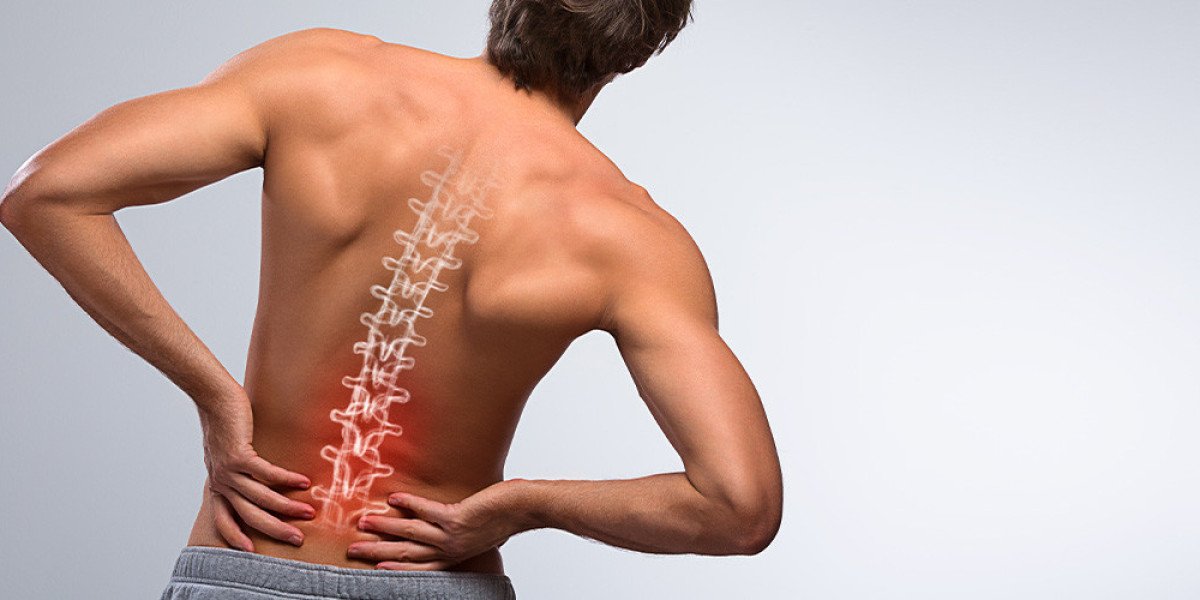
Pain is a complex sensation that serves as a signal from the body, indicating that something may be wrong. While most pain is temporary and can be managed with rest, medication, or other interventions, there are instances when pain may indicate a serious underlying condition that requires urgent medical attention.
Topcynta 100mg is often prescribed for pain that is severe and not adequately controlled by other medications or treatment modalities.
In this blog, we will explore the different types of pain that may be considered serious, the red flags to watch out for, and the appropriate steps to take when encountering such pain.
Understanding Serious Pain
Serious pain is typically characterized by its intensity, persistence, and impact on daily life. Unlike minor aches and pains that may resolve on their own or with self-care measures, serious pain often indicates an underlying health issue that requires prompt evaluation and treatment by a healthcare professional.
Types of Serious Pain
Serious pain can manifest in various forms, each associated with different underlying conditions. It's important to recognize that Aspadol 100mg, like other opioid medications, carries potential risks and side effects. These may include dizziness, drowsiness, nausea, constipation, respiratory depression, tolerance, dependence, and addiction.
Some common types of serious pain include:
Chest Pain:
Chest pain can be a symptom of numerous serious conditions, including heart attack, angina, pulmonary embolism, aortic dissection, or pneumonia. It may present as pressure, tightness, burning, or sharp stabbing pain and may radiate to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or abdomen.
Chest pain is often associated with heart-related issues, such as:
Heart Attack: Also known as myocardial infarction, a heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked, leading to damage or death of heart muscle tissue. Symptoms may include pressure, tightness, squeezing, or burning pain in the chest, along with shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, lightheadedness, or pain radiating to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or abdomen.
Angina: Angina is chest pain or discomfort that occurs when the heart muscle doesn't receive enough oxygen-rich blood. It may feel like pressure, squeezing, heaviness, or tightness in the chest and can be triggered by physical exertion or stress. It typically subsides with rest or medication.
Pericarditis: Pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, the thin sac surrounding the heart. It may cause sharp, stabbing chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or lying down and improves when leaning forward. Other symptoms may include fever, cough, and fatigue.
Abdominal Pain:
Abdominal pain can be caused by gastrointestinal issues such as appendicitis, pancreatitis, gallstones, intestinal obstruction, or inflammatory bowel disease. It may vary in severity and location and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or fever.
Common Causes of Abdominal Pain:
Abdominal pain can be caused by a wide range of conditions, including:
Gastrointestinal Issues: Conditions such as gastroenteritis, gastritis, peptic ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), or constipation can cause abdominal pain, bloating, cramping, and changes in bowel habits.
Gallbladder Disorders: Gallstones, cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder), or biliary colic can lead to sharp, intense pain in the upper right abdomen, often radiating to the back or shoulder blades.
Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can cause severe, persistent abdominal pain, often radiating to the back, along with nausea, vomiting, fever, and tenderness.
Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix can cause sudden, severe pain in the lower right abdomen, often accompanied by fever, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections of the urinary tract, including cystitis (bladder infection) or kidney infection, can cause lower abdominal pain, burning with urination, urinary urgency, and frequency.
Reproductive Issues: In women, conditions such as ovarian cysts, endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), or ectopic pregnancy can cause abdominal pain, pelvic discomfort, abnormal vaginal bleeding, or changes in menstrual patterns.
Headache:
While most headaches are benign and can be attributed to factors like tension, dehydration, or sinus congestion, severe or sudden-onset headaches may indicate more serious conditions such as migraine with aura, cluster headaches, intracranial bleeding, or meningitis.
Back Pain:
Back pain is a common complaint that can result from muscle strain, poor posture, or mechanical issues. However, persistent or severe back pain may be indicative of spinal problems such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, compression fractures, or tumors.
Joint Pain:
Joint pain can occur due to arthritis, autoimmune diseases, infections, or traumatic injuries. While mild joint pain is common, severe or sudden-onset joint pain accompanied by swelling, redness, warmth, or fever may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Red Flags for Serious Pain
Certain warning signs or red flags may indicate that pain is more than just a minor inconvenience and requires urgent medical attention. These red flags include:
- Sudden onset or severe intensity of pain.
- Pain that persists or worsens despite rest or treatment.
- Pain is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, shortness of breath, chest tightness, weakness, numbness, or loss of consciousness.
- Pain that radiates to other areas of the body or is associated with changes in bowel or bladder function.
- Pain following trauma, injury, or recent surgery.
- Pain in specific populations such as older adults, pregnant women, or individuals with underlying health conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It's essential to seek prompt medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Chest pain, especially if it radiates to the arm, jaw, or back, or is accompanied by sweating, shortness of breath, or nausea.
- Severe abdominal pain, particularly if it's sudden or persistent is associated with fever, vomiting, or blood in the stool.
- Sudden or severe headache, especially if it's accompanied by confusion, weakness, slurred speech, or vision changes.
- Back pain with numbness or weakness in the legs, difficulty walking, or loss of bowel or bladder control.
- Joint pain with swelling, redness, or warmth, especially if it's sudden or affects multiple joints.
Conclusion
Serious pain is a warning sign from the body that should not be ignored. While minor aches and pains are common and often resolve on their own, certain types of pain may indicate a serious underlying condition that requires urgent medical attention.
By understanding the different types of serious pain, recognizing red flags, and knowing when to seek medical help, individuals can ensure timely evaluation and treatment, potentially preventing further complications and promoting better health outcomes.
Remember, when it comes to pain, it's better to err on the side of caution and seek professional medical advice when in doubt.