The requirement for improving the billing accuracy in the service sector, such as government buildings, private offices, and data centers, propels efficient and smart monitoring and control devices. Owing to such benefits, smart meters have become part of numerous government projects worldwide that aim to improve billing accuracy. For example, in India, under the government's Smart Meter National Programme, state-owned company EESL announced the successful installation of around one million smart meters in February 2020.
Smart meters are capable of supporting a bi-directional flow of information. They are operated at the end user's property to gather information about the electricity usage of various appliances at regular intervals. Utility centers can easily send commands, information, or signals to the meter installed at end users' premises, whenever required. Similarly, the users of these devices can automate various appliances, such as washing machines, TVs, and ACs. Thus, they enable time-of-use tariffs, which impel people to reduce their energy consumption during peak load durations, when electricity, gas, and water are the costliest.
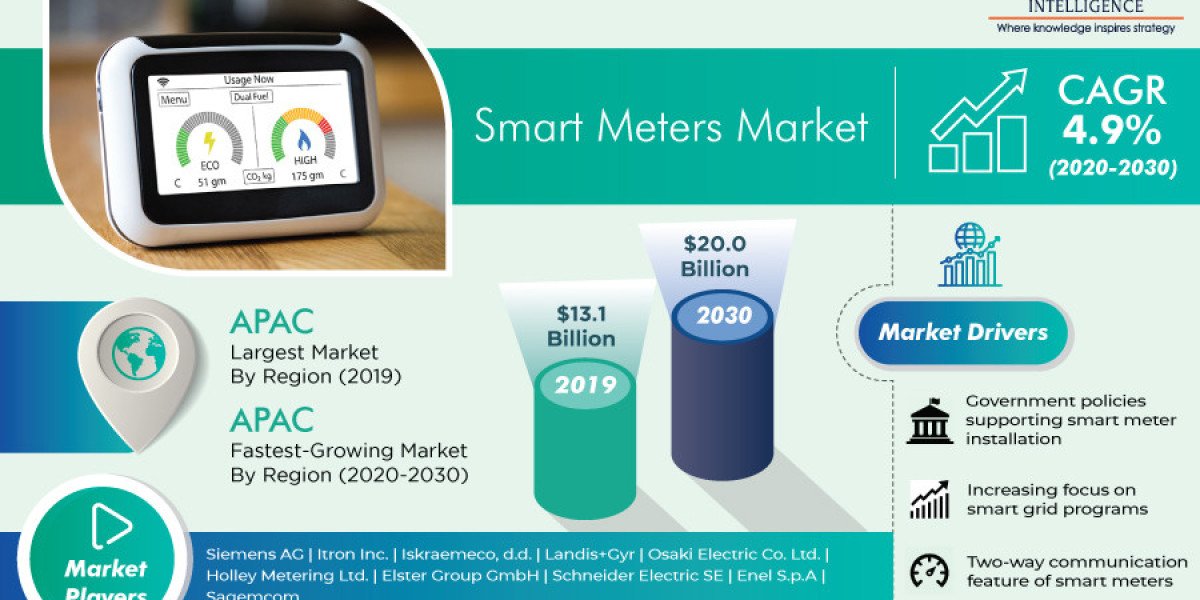
The smart meters market is therefore set to value $20.0 billion in 2030 , growing from $13.1 billion in 2019 at a 4.9% CAGR during this decade. Among smart electric, gas, and water meters, the demand for water meters is set to rise the fastest in the coming years. It is attributed to the emerging usage of these devices by consumers and even utilities for keeping track of their water consumption and monitoring the pressure, wastage, and leakage of this precious resource. Furthermore, smart water meters carry out data analysis for optimizing the resource's usage.
In this regard, the increasing awareness about the depleting water resources is contributing to the adoption of smart meters. “Four billion people — almost two-thirds of the world's population — experience severe water scarcity for at least one month each year.”, says UNICEF. The UN agency also says that by 2025, more than 50% of the global population could experience water scarcity if proper water wastage control and conservation measures aren't taken.
As the same is the case with natural gas and the fuels burned for generating electricity, the residential sector is the largest user of smart meters. With the rapid urbanization, the consumption of gas, water, and electricity is burgeoning, which is leading to their rising prices. Thus, urban residents are installing smart meters to check their resource usage in real-time, get an idea of the bill, and make concrete efforts to reduce their energy, water, and gas consumption.
This is why globally, Asia-Pacific (APAC) is expected to dominate the smart meters market in the coming years. Additionally, in several countries of the region, the government has taken initiatives for installing these devices. This is attributed, in part, to the shifting inclination toward the modernization of the grid network. For instance, China has a five-year nationwide plan to upgrade the grid infrastructure with smart meters. Essentially, countries in the APAC region are adopting these devices to address their energy challenges and improve the utility revenue collection process.
Therefore, the growing need for conserving gas, water, and electricity will propel the deployment of smart meters globally in the coming years.
Source: P&S Intelligence